A well-defined innovation process is crucial for companies to maintain competitiveness and achieve sustainable growth. While the specifics may vary across industries, the best innovation operating models share common characteristics: they are structured, repeatable, and fit the conditions.
In this article, we explore six of the most effective innovation processes used by leading organizations. We’ll look at how key practices like digital ideation, open innovation, collaboration, venture clienting, and incremental innovation drive successful outcomes and how they affect innovation processes.
What is an innovation process?
Innovation is the process of bringing about new ideas, methods, products, services, or business models that have a significant positive impact and value. It involves transforming creative concepts into tangible outcomes that improve efficiency, and effectiveness, or address unmet needs.
Innovation is not limited to technological advancements; it encompasses novel approaches to problem-solving, processes, organizational practices, or business model innovations. At its core, innovation involves challenging the status quo, thinking outside the box, and taking calculated risks to drive progress and achieve breakthrough outcomes.
Whether it’s developing a new product, optimizing a business model, or finding a more efficient way to operate, innovation is the driving force behind sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
An innovation process, or process of innovation, outlines how companies generate, evaluate, and implement new ideas (Exhibit 1). Clearly defining innovation objectives is crucial for guiding the innovation process effectively. It typically involves multiple stages, from brainstorming to validation and implementation. Successful innovation operations help organizations improve existing operations, develop new products, and respond to market changes efficiently.

Exhibit 1: The innovation process
An innovation process based on systematic steps and strategies ensures leadership commitment, resource allocation, and an organizational culture that promotes creativity and cross-functional collaboration.
Key steps in the innovation process
Innovation stage 1: Opportunity identification
The innovation process is a structured approach that helps organizations develop and implement new ideas effectively. It begins with identifying opportunities. This step involves looking for areas where innovation can create value, whether through market research, customer insights, or trend analysis. Internal assessments can also reveal gaps where new solutions could have a significant impact.
Innovation stage 2: Idea collection and generation
Once opportunities are identified, the next step is to engage in idea generation through structured approaches. This often happens through brainstorming sessions, idea competitions, or collaborative efforts across departments. Innovative idea generation is crucial in this phase, focusing on the pursuit of groundbreaking ideas that can transform products and services. The more diverse the input, the better the range of ideas, as different perspectives can spark more creative and impactful solutions.
Innovation stage 3: Idea refinement, evaluation, and prioritization
After generating a wide pool of ideas, it's time to evaluate and select the most promising ones. This involves assessing each idea based on its market potential, technical feasibility, resource requirements, and alignment with the company’s strategic goals. By carefully evaluating these factors, companies can ensure they focus on the ideas most likely to succeed.
Innovation stage 4: Development and prototyping
The selected ideas are then taken into development and prototyping. At this stage, the concepts are turned into tangible models, whether through prototypes, mock-ups, or minimum viable products (MVPs). This allows the organization to test the core features of the idea before fully committing resources.
Innovation stage 5: Testing and iteration
Next comes the testing and iteration phase. Prototypes or MVPs are tested with real users or in controlled environments to gather feedback. This step is crucial because it helps refine the product or service to better meet customer needs and expectations. Adjustments are made based on this feedback, improving the chances of success when the innovation is fully launched.
Innovation stage 6: Implementation and scaling
When the innovation has been validated, it’s time to implement innovation and scale. This requires careful planning, resource allocation, and execution to bring the innovation to market. Scaling the innovation means ensuring that it can be successfully rolled out across broader markets or integrated into existing operations.
Innovation stage 7: Lifecycle management
Finally, after the innovation is in place, the process doesn’t end. Companies need to monitor and evaluate their performance. By tracking key metrics and performance indicators, organizations can assess the impact of the innovation and identify any areas that need further improvement. This ongoing evaluation helps ensure long-term success and informs future innovation efforts.
The benefits of a systematic innovation process
A structured innovation process offers several key benefits that drive more effective and sustainable outcomes for organizations. First, consistency ensures that innovation activities follow a predictable and repeatable approach. This standardization across teams reduces variability, leading to higher-quality outcomes and ensuring that no valuable ideas fall through the cracks. A consistent process helps maintain focus and ensures that innovation is treated as a continuous, ongoing effort rather than a sporadic initiative.
Another significant advantage is transparency. When there’s a clear framework in place, everyone within the organization can see how ideas are evaluated, prioritized, and moved forward. This visibility fosters trust and encourages participation, as teams understand the criteria used for decision-making. Transparency also makes it easier to track the progress of innovation initiatives, providing insight into which projects are succeeding and why.
Better resource management is another critical benefit. With a structured process, companies can allocate their time, budget, and personnel more efficiently. By evaluating and prioritizing ideas systematically, they can focus resources on the most promising opportunities, avoiding wasted effort on projects that are unlikely to succeed. This leads to more strategic use of resources and reduces the risk of overcommitting to underperforming ideas.
Additionally, a defined process accelerates faster time-to-market. By streamlining the stages of ideation, prototyping, and implementation, companies can bring new products and services to market more quickly. Clear steps and decision points eliminate bottlenecks, allowing teams to act decisively and efficiently, which is especially important in industries where speed is critical to maintaining a competitive edge.
A structured approach also ensures alignment with strategic objectives. By integrating the innovation process with broader company goals, organizations can ensure that their innovation efforts are directly contributing to long-term success. Each stage of the process is tied back to the company’s strategic vision, ensuring that resources are focused on initiatives that align with key priorities.
Finally, structured innovation enhances collaboration across teams and departments. A well-defined process encourages cross-functional participation, breaking down silos and bringing together diverse perspectives. Utilizing collaboration tools further enhances this collaboration by enabling communication, experimentation, and the exchange of ideas among team members. This improves the quality of ideas and leads to more holistic and impactful solutions. Enhanced collaboration ensures that innovations are not only technically feasible but also align with market needs and operational capabilities.
Together, these benefits create a more effective and focused innovation process that drives a joyful innovation journey.
The industries' roles in shaping the perfect innovation process
The pace and structure of innovation within a company are heavily influenced by the industry it operates. While many businesses aim to streamline their innovation process, the nature of their sector often dictates how they innovate, how fast they need to act, and the specific challenges they face. Understanding the role of industry is critical for businesses to tailor their innovation efforts effectively (Exhibit 2).
.webp?width=1200&height=679&name=Unleashing-Speed-Strategies-to-Slash-Time-to-Market-3%20(1).webp)
Exhibit 2: The roles of industries tailoring innovation efforts
Innovation cycles vary by industry
Different industries experience vastly different innovation cycles. In fast-moving sectors such as technology, software, and consumer electronics, disruptive innovation happens at a rapid pace. These industries are characterized by short product lifecycles, constant demand for updates, and the pressure to bring new solutions to market quickly. A software company, for instance, may develop and deploy updates within weeks, and consumer electronics firms often release new models annually. Continuous technological advancements and high consumer expectations for the latest features drive the speed at which these industries support innovation initiatives.
In contrast, industries like pharmaceuticals and aerospace follow much longer innovation cycles. The development of new pharmaceuticals often takes a decade or more due to extensive research, clinical trials, and regulatory approvals. Similarly, aerospace innovations require precise engineering, safety considerations, and adherence to stringent regulatory frameworks, extending the time-to-market. In these sectors, the innovation process is more cautious and deliberate, reflecting the high stakes and complexity involved.
Regulatory and market dynamics in innovation strategy
Regulatory requirements also play a crucial role in shaping innovation processes. In highly regulated industries like healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace, companies must navigate complex approval processes before bringing a new product or service to market. This not only lengthens the innovation cycle but also requires companies to integrate compliance and safety testing into their processes from the start. Companies in these industries must balance innovation with the necessity of meeting rigorous standards, which can slow down their overall pace of development but ensure safety and reliability.
Conversely, industries like consumer goods and retail, where regulations are less stringent, can afford to move faster. These sectors tend to have more flexible innovation processes, allowing companies to iterate and launch new products quickly to meet evolving consumer demands. However, even in these less-regulated industries, businesses must adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences, ensuring that their innovation process remains responsive and agile.
Digital transformation across industries
While industry-specific factors like regulation and market dynamics heavily influence the innovation process, digital transformation is impacting all sectors. Companies in traditional industries like manufacturing, automotive, and even pharmaceuticals are increasingly integrating digital tools into their innovation process. This transformation allows for faster ideation, prototyping, and testing, which speeds up time-to-market across the board. Industries that once moved at a slower pace are now leveraging digitalization to innovate more efficiently and stay competitive.
For example, manufacturers are adopting automation and artificial intelligence to optimize product development and reduce production times. In healthcare, digital tools are helping streamline drug discovery and trial processes. Digital transformation is shortening innovation cycles across many sectors, but the degree to which it affects each industry varies depending on the specific challenges and constraints they face.
The best innovation process examples
Here are examples of companies that have optimized their innovation processes to deliver measurable results.
Example 1: VNTR - PostFinance
Innovation process example 1: Horizon 3 innovation process
A horizon 3 innovation process aims for innovation that goes beyond the current core (Exhibit 3). It is the horizon of transformative and radical innovation. We saw the following innovation process with VNTR—the innovation and venturing unit at PostFinance.
Anchoring its decision-making in strategic foresight, VNTR begins the innovation process by identifying and exploring relevant signals, trends, and technologies. This foresight phase aims to derive new fields of innovation that may hold potential new opportunities for PostFinance.
The validation phase bridges strategic foresight with operational scalability. It involves rapid market experiments to test feasibility and customer needs. Defined hypotheses are rigorously verified or falsified, ensuring a smooth transition from ideation to operation. Validated hypotheses propel projects toward the final phase.
.webp?width=957&height=612&name=PostFinance_Innovation%20Process%20(1).webp)
Exhibit 3: A horizon 3 innovation process
VNTR's final phase focuses on efficiently scaling initiatives for sustained growth, within or beyond the organization. It entails implementing validated innovations, optimizing processes, and adapting strategies for long-term success in dynamic markets.
VNTR rigorously evaluates every innovation project through a phase-gate process—not all emerge successfully. At each gate, and continually based on evolving insights, decisions are made: to proceed with enthusiasm (love it), refine as needed (change it), or discontinue (leave it) with informed judgment.
Twice yearly, VNTR hosts a collaborative workshop to define new innovation fields using trends and insights. Opportunities emerging from this session are presented at Gate 0, defining upcoming topics for exploration and steering VNTR's future actions.
Example 2: DB Schenker
Innovation process example 2: Elaborate Innovation Management
Another effective innovation strategy is combining customer pain point insights (micro signals) and trend analysis (macro signals). This process involves continuously monitoring both internal and external sources for signals of change. Once insights are identified, they guide the organization’s innovation priorities. We saw this process with DB Schenker - one of the world’s leading logistics service providers.
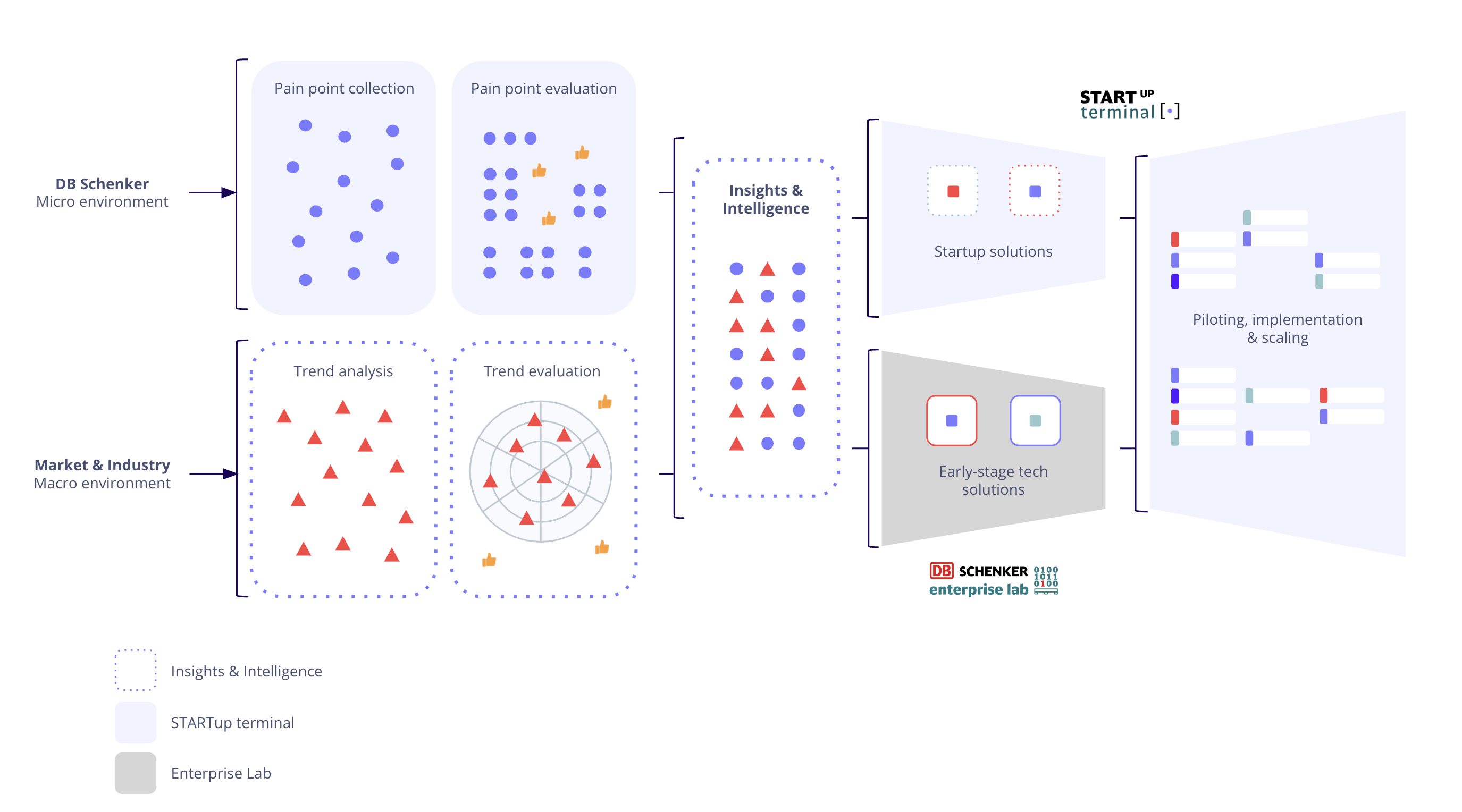
DB Schenker's innovation process is quite elaborate. Yet, before working with ITONICS, it managed its innovation activities with disparate tools: Jira for tracking startups, PowerPoint for trend analysis, and various project management applications. Teams, often working on interrelated yet distinct projects, struggled to align and share critical knowledge. With the STARTup terminal engaged in venture clienting, the Enterprise Lab exploring new tech solutions, and the Insights & Intelligence Team analyzing trends to guide the strategic focus across business units—DB Schenker needed one centralized tool to streamline the flow of innovation - and found it with ITONICS the Innovation OS.
Example 3: Merz
Innovation process example 3: R&D-driven innovation projects with rigorous validation
In industries such as healthcare, where safety and efficacy are critical, research and development (R&D) play a central role in the innovation process. The focus is on rigorous validation, ensuring that all new products or services meet high standards of quality and compliance. This approach requires close collaboration between R&D and marketing teams to ensure that innovations pass regulatory scrutiny and meet market demands. We saw the following innovation process at Merz - an internationally active, family-owned pharmaceutical company.

To determine the competitive landscape of the current portfolio, predefined search fields are used to collect knowledge from various sources:
-
Companies and their products as well as clinical trials, patents, publications
-
Internet searches, press releases, conferences, market reports
-
Employee contributions on specific topics, e.g. indications like Parkinson‘s disease or technologies like neurostimulation/-modulation devices
-
External experts who input data on emerging products and technologies
The collected insights are enriched by the AI-enabled signals feed, which automatically adds relevant market signals to the scouted products and companies. Other departments can additionally access, edit, and supplement the data. The most relevant products and companies are assigned to a specific technology field or indication and selected for further evaluation.
The hits are evaluated by the Scouting Team and experts from other departments. Evaluation criteria include, for example, the efficiency or the safety of a treatment. The evaluated results can be visualized in different Radars and provide the Screening Team and Business Development Board with evidence to make better strategic decisions on portfolio expansions.
Example 4: Sartorius
Innovation process example 4: Corporate research’s innovation process
A corporate research department enhances early-stage innovation initiatives. The objective is on the collaborative, multidisciplinary development of technologies up to the proof-of-concept (PoC) stage. We saw the following early innovation process with Sartorius. The department at Sartorius recognized that valuable knowledge and expertise were distributed across different locations within the organization. Geographic and time zone differences posed challenges to productive technology discussions.
Additionally, there was a clear need to validate new technologies at the PoC stage before committing to long-term development roadmaps. The department aimed to better understand the landscape of emerging trends and technologies that would be essential for the company’s future success.
Sartorius utilized the ITONICS Innovation OS to scout, document, and categorize its innovation intelligence. This encompassed a broad spectrum, from emerging technologies and potential partners to active projects and prospective opportunities. The flexible and customizable structure of the Innovation OS enabled rapid capture and systematic organization in alignment with Sartorius’ internal best practice. This ensured immediate access to crucial information for the Corporate Research innovation team and internal stakeholders.
To visualize and evaluate its scouting efforts, Sartorius used the ITONICS Radar visualization. The Radar provides a holistic view of relevance and impact, helping to identify areas requiring further focus and action. The platform's sharing and commenting capabilities allow for ongoing, tracked discussions for a globally distributed innovation team across multiple time zones. By allowing members to score these elements according to business impact, priority, or strategy fit, Sartorius was able to focus its resources and efforts on the most promising areas, ensuring alignment with innovation objectives.
Sartorius’ innovation program comprises both internal and external technology development capabilities. Based on the evaluation, the right action channel is chosen and innovation initiatives are set up. The system sped up the identification of potential partners, particularly startups and academic groups, that align with current or future business models, thereby fostering collaborative opportunities.
Example 5: Alliance SwissPass
Innovation process example 5: End2end innovation process
In industries where multiple players must work together—such as public infrastructure or transport—an innovation team is essential for structured processes and ongoing management. By bringing together stakeholders from across the value chain, organizations ensure that their innovations are practical, sustainable, and scalable. This process typically involves fostering an organizational culture that values creativity and collaboration, leading to the generation and evaluation of innovative ideas through frequent collaboration with policymakers, customers, and industry partners.
One of the strengths of this approach is the ability to create solutions that meet the needs of all stakeholders, from end users to regulatory bodies. An innovation project that arises from these collaborations is typically aligned with broader societal goals, such as sustainability or accessibility. This ensures a higher rate of adoption and long-term success. We saw the following innovation process example with Alliance SwissPass, an association of transport companies in Switzerland.
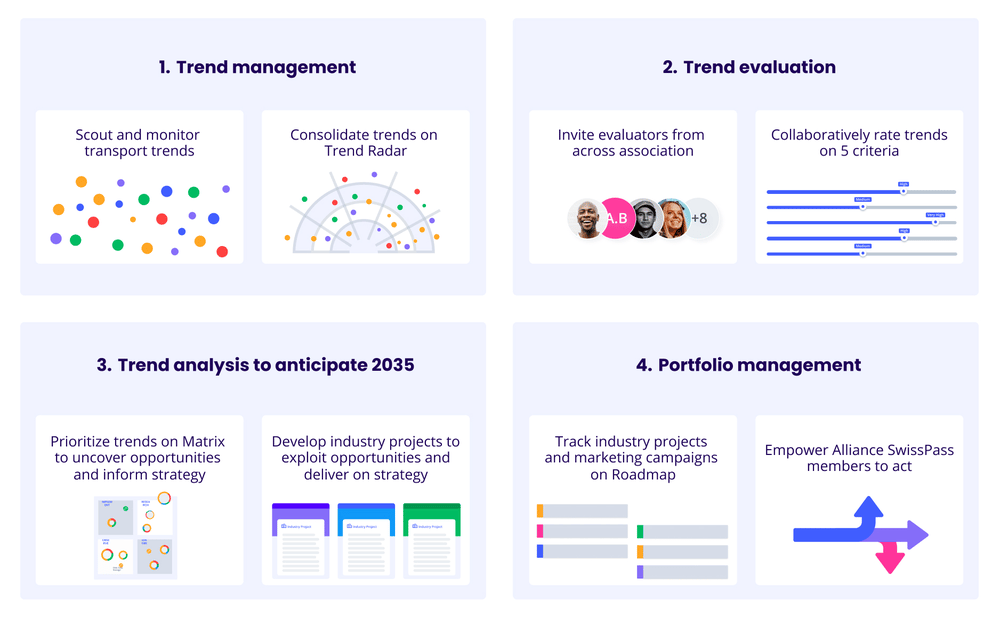
1. Trend management: Alliance SwissPass has a well-established and proven trend management process with the Trend Radar at its core. After identifying relevant trends from industry research, publications, and the ITONICS trend collection, the Radar consolidates and organizes them for easy engagement and interpretation. Thanks to the platform’s flexibility, each company can also create and manage its own Trend Radar that is uniquely specific to its innovation objectives and strategy.
2. Trend evaluation: Trend evaluation at Alliance SwissPass is collaborative and constructive, involving representatives from multiple companies to leverage diverse perspectives and expertise across the association. With configurable ratings in ITONICS, trends are evaluated on five criteria: overall maturity, time to adaptation, added value to corporate division, adaptation status, and added value for public transport customers.
3. Trend analysis: Based on the trend ratings, Alliance SwissPass uses the Matrix to gain a prioritized view of the trends with the greatest potential impact. Equipped with this foresight intelligence, Alliance Swiss Pass formulates a shared vision of the future of public transport and mobility in Switzerland, looking ahead to 2035. Achieving this long-term vision means turning identified opportunities into actionable projects and aligning efforts across the association’s diverse membership.
4. Portfolio management: Alliance SwissPass’ portfolio of industry projects has become its greatest driver of engagement in the Innovation OS. With this single source of truth, all members can access the portfolio, track project progress, and visualize the 2035 strategy on an agile Roadmap. They also gain a holistic view of the trends and committee decisions that inform the strategy and marketing campaigns for launching new offerings. This transparency empowers members to align their activities accordingly and collectively drive continuous innovation in Swiss mobility.
Example 6: KSB
Innovation process example 6: Global idea management for continuous improvement
For companies with a global footprint, centralizing the innovation process through a single platform allows for better coordination across regions and helps evolve the business model to address customer needs and maintain a competitive edge. This approach standardizes the way innovative ideas are collected, evaluated, and implemented, ensuring that innovations developed in one region can be scaled globally.
Centralizing the innovation process also helps in fostering an innovative culture that supports and encourages innovation across all levels of the company. Together with ITONICS, KSB has built a digital backbone for global knowledge and innovation management.

With the new process, it is now possible to identify strategic innovation fields for growth in possible attractive markets and generate new ideas accordingly. On the other hand, individual idea campaigns can be initiated to collect ideas from global participants.
Facilitating a smooth innovation process with the right innovation management software
The ITONICS Innovation OS is the best innovation management software to run a successful innovation process. At ITONICS, we understand the importance of innovation and offer a comprehensive innovation management platform.
/Still%20images/Portfolio-product-header-1000px.webp?width=1000&height=629&name=Portfolio-product-header-1000px.webp)
Our Innovation OS embodies all the essentials of the best innovation management software and covers all the application areas in one tool. It will help you to:
-
Eliminate Information Silos:
Dispersed teams and disconnected data often result in missed opportunities and duplicated efforts. With ITONICS, all your innovation projects, most innovative ideas, and market insights are centralized in one place. Create transparency and reduce inefficiencies by keeping everyone on the same page. -
Streamline Idea Management:
Managing a high volume of ideas from various sources can be overwhelming. ITONICS allows you to capture, evaluate, and prioritize ideas from across the organization, including customers and partners, all in one structured process. This helps focus resources on the most impactful ideas and reduces time wasted on less promising ones. -
Track innovation progress across teams:
Monitoring the progress of multiple innovation projects across departments isn’t easy. ITONICS provides visual dashboards and automated reporting tools that give you a real-time overview of ongoing projects, ensuring you can quickly address roadblocks, identify risks, and keep everything on track. -
Foster a culture of innovation:
Innovative breakthroughs often come from collaboration. ITONICS enables your teams to collaborate in real time, regardless of location, by sharing insights, feedback, and updates directly within the platform. This fosters a culture of innovation where great ideas can emerge from any corner of your organization.
FAQs on the best innovation process
What is an innovation process?
An innovation process is the structured series of activities an organization follows to generate, evaluate, and implement new ideas that create measurable value.
What are the key stages of the innovation process?
The seven key stages of the innovation process are:
1. Opportunity identification
2. Idea generation
3. Idea refinement & prioritization
4. Development & prototyping
5. Testing & iteration
6. Implementation & scaling
7. Lifecycle management
Typically, each organization uses its vocabulary to describe the stages or summarizes some of the activities in fewer stages.
Why does a company need a structured innovation process?
A repeatable framework increases transparency, speeds time-to-market, focuses resources on high-impact ideas, and aligns innovation work with strategic objectives.
Which innovation process models do leading organizations use?
The best innovation process depends on the organization's history, ambition, and industry characteristics. Leading organizations adapt the pace and rigor of the innovation process to these factors.
What are real-world examples of successful innovation processes?
Real-world examples of innovation processes are:
- Sartorius uses a scouting-to-PoC flow,
- Alliance SwissPass runs an end-to-end multi-stakeholder model, and
- KSB employs a global idea-management backbone to scale continuous improvement.
How does innovation management software support innovation processes?
A platform like ITONICS Innovation OS centralizes insights, streamlines idea capture and evaluation, tracks progress, and fosters collaboration across global teams.
Innovation management software facilitates the execution and full compliance of the innovation process model.
How can digital platforms drive innovation process standardization?
Digital platforms like ITONICS enable innovation process standardization by centralizing data, structuring workflows, and ensuring consistent idea evaluation and execution across teams. This ultimately leads to greater transparency, efficiency, and alignment.
How can organizations drive cross-functional innovation processes digitally?
Organizations can use digital platforms like ITONICS to connect teams, centralize data, and standardize workflows. This enables structured, cross-functional collaboration throughout the innovation process.