LEGO revitalized its innovation strategy by launching LEGO Ideas, a platform where fans submit designs for new sets. By tapping into external creativity, LEGO transformed user-generated concepts into bestsellers, such as the LEGO Saturn V rocket, while fostering deep engagement with its community. This approach allowed the company to source fresh ideas, test market demand before production, and build deeper connections with its consumers.
Industry leaders showcase practical applications and investments in open innovation through various open innovation examples, driving new ideas and advancements.
Yet, many companies still hesitate to embrace open innovation, fearing intellectual property risks, integration challenges, and loss of control. In today’s dynamic market, relying solely on internal R&D limits growth, speed, and adaptability. Businesses that fail to engage external networks often struggle to keep pace with rapid technological advancements and shifting consumer expectations.
This article explores how companies can successfully implement open innovation, drawing from real-world examples, strategic approaches, and practical tools that help organizations collaborate, reduce development costs, and accelerate breakthrough innovations.
What is open innovation
Open innovation is a business strategy that leverages external knowledge, ideas, and technologies to foster innovation. Unlike traditional closed R&D, where companies rely solely on internal expertise, open innovation encourages collaboration with startups, universities, suppliers, customers, and even competitors to accelerate product development, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
The concept was popularized by Henry Chesbrough in 2003, who argued that organizations must look beyond their internal boundaries to remain competitive in an era of rapid technological change. Companies that adopt open innovation actively seek external solutions, co-develop new technologies, and engage in knowledge-sharing partnerships to stay ahead.
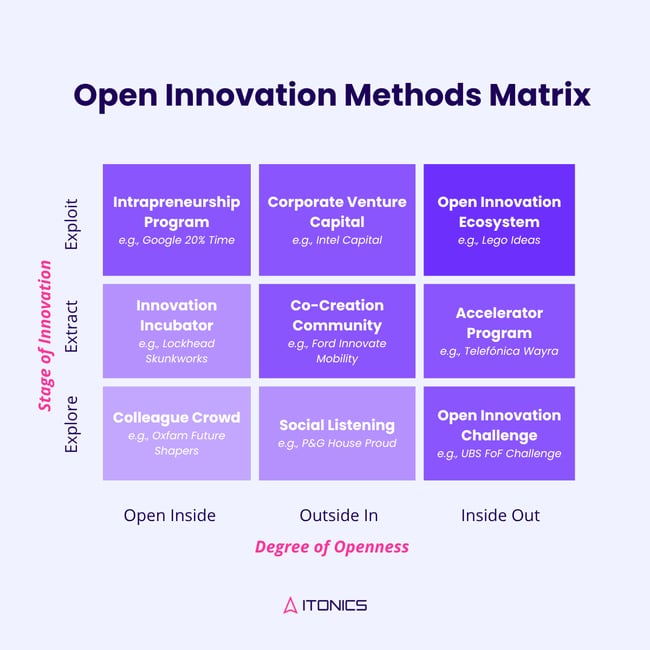
Exhibit 1: Open Innovation Methods Matrix
Open innovation takes different forms, including crowdsourcing, where businesses invite ideas from the public, and strategic partnerships, where firms share R&D resources. For example, Unilever’s Open Innovation platform allows researchers and entrepreneurs to propose solutions for sustainability and product development. Similarly, Tesla’s open-patent policy has encouraged widespread EV advancements by allowing competitors to build on its technology.
By embracing the open innovation model, which includes approaches such as outside-in and inside-out innovation, and understanding the distinctions between open and closed innovation, companies enhance agility, expand their expertise, and accelerate time-to-market, turning external suggestions into market-ready solutions. As industries evolve, businesses that integrate open innovation effectively will be better positioned for long-term success.
Benefits of open innovation
Open innovation enables companies to tap into external expertise, accelerate R&D, and reduce costs by collaborating with startups, universities, customers, and industry experts. Instead of relying solely on internal resources, businesses can leverage a diverse range of perspectives and expertise to drive innovation faster and more effectively.
One of the biggest advantages is faster time-to-market. By sourcing ideas externally, companies can shorten development cycles and launch new products more quickly. For example, LEGO Ideas allows fans to submit product concepts, helping the company introduce highly desired sets with minimal internal R&D investment.
Open innovation also reduces costs and risks. Sharing development efforts with external partners minimizes the financial burden and lowers failure rates. Platforms like Unilever’s Open Innovation Program help the company find sustainable solutions globally while optimizing R&D spending.
Additionally, collaboration fosters breakthrough innovations. Companies can access specialized expertise they lack internally, allowing them to integrate cutting-edge technologies and respond more effectively to industry shifts. Tesla, for instance, shared its electric vehicle patents to accelerate industry-wide innovation while maintaining its competitive edge.
By embracing open innovation, businesses enhance creativity, build strategic partnerships, and stay ahead of competitors, making it an essential strategy for long-term success.
When to use open innovation vs. closed innovation
Innovation is essential for business growth, but choosing between open innovation and closed innovation depends on the company’s goals, industry dynamics, and competitive landscape (Exhibit 1). While both approaches have their advantages, understanding when to use each is critical for long-term success.
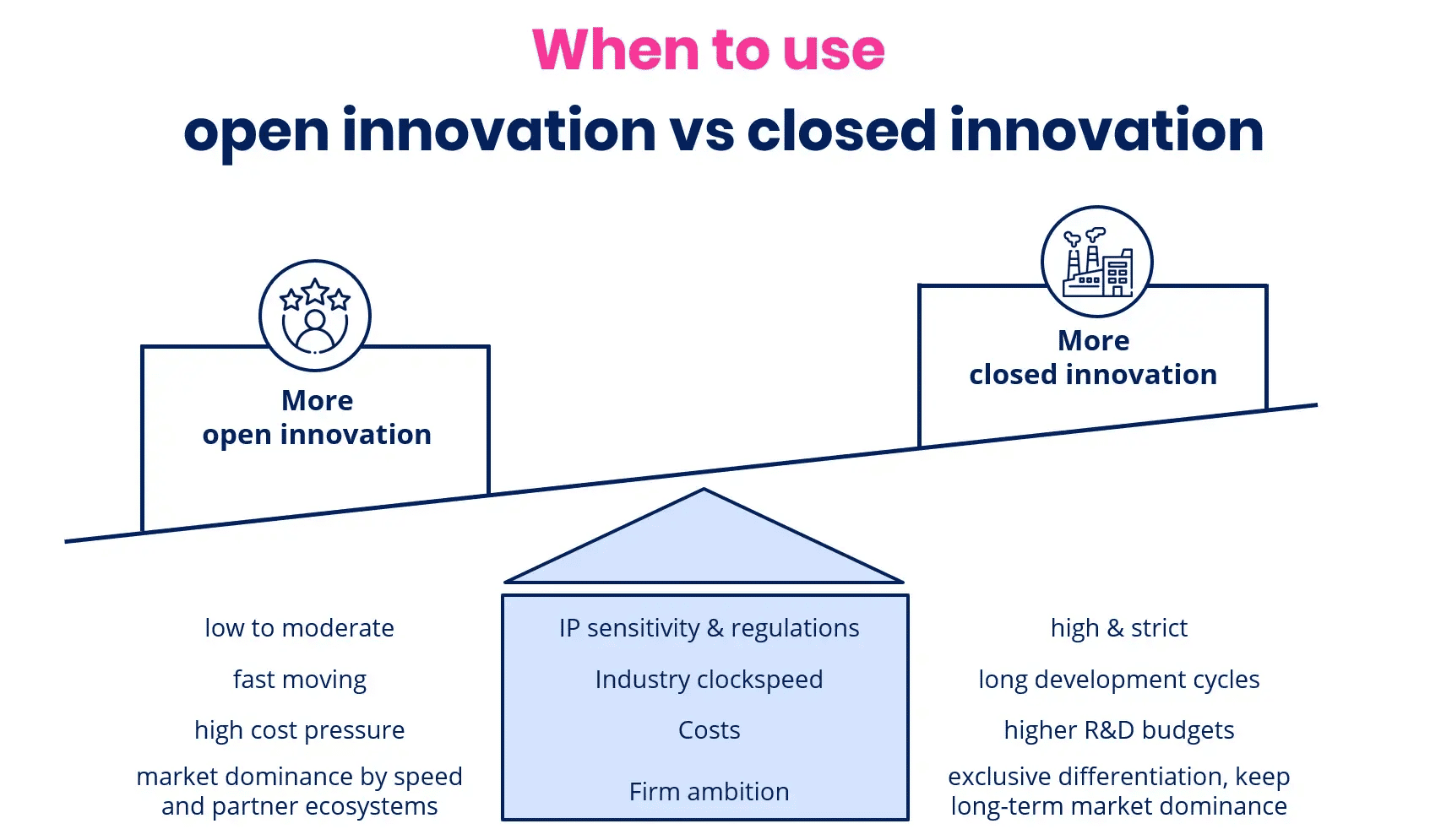
Exhibit 2: The difference in when using open vs. closed innovation
When to use open innovation
Open innovation is most effective when companies need fresh perspectives, external expertise, or faster development cycles to solve complex problems. It works well in industries that require rapid technological advancements or when internal resources are insufficient to solve complex challenges.
Fast-changing markets: In industries like technology, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, external collaboration helps companies keep up with shifting trends. LEGO Ideas, for instance, taps into fan creativity to co-develop products.
Cost and risk reduction: Sharing R&D efforts with startups, universities, or industry partners reduces the financial burden. Unilever’s Open Innovation Program sources sustainable solutions globally, reducing research costs.
Access to specialized expertise: Some innovations require knowledge beyond a company’s core competencies. Tesla’s open-patent strategy accelerates electric vehicle adoption by enabling collaboration.
When to use closed innovation
Firm-led innovation is preferable when proprietary knowledge, competitive differentiation, or security concerns are top priorities. This model ensures greater control over intellectual property and product development.
High IP sensitivity: In industries like aerospace, defense, and high-tech manufacturing, companies protect their breakthroughs to maintain competitive advantage.
Regulatory and compliance constraints: Sectors such as biotechnology and finance often require stringent oversight, making closed innovation necessary to meet legal and security requirements.
Strong internal R&D capabilities: Companies with significant in-house expertise, like Apple, develop proprietary technologies without external input to maintain brand differentiation.
Ultimately, the choice depends on innovation goals, industry conditions, and risk tolerance. Many businesses adopt a hybrid approach, combining both strategies to maximize competitive advantage while maintaining security and control.
Why companies are shifting toward open innovation
The traditional model of innovation, where companies rely solely on firm-led R&D, is becoming less sustainable in today’s fast-changing, highly competitive business environment. Companies are increasingly turning to open innovation to accelerate development, reduce costs, and access external expertise that would be difficult to cultivate in-house.
Open innovation is crucial for digital transformation and company growth, enabling organizations to innovate and stay competitive in the market.
One key driver of this shift is the growing complexity of technology. Many industries, such as AI, biotechnology, and renewable energy, require cross-disciplinary expertise that no single company can master alone. By collaborating with startups, universities, and industry partners, businesses can tap into specialized knowledge without building it from scratch.
Another factor is cost and risk reduction. Developing new products or technologies internally is expensive and uncertain. Open innovation allows companies to share development costs, reduce failure rates, and gain market insights early. For example, Unilever’s Open Innovation Program helps the company source cutting-edge sustainability solutions globally, avoiding high R&D expenses.
Additionally, consumer expectations are evolving rapidly. Open innovation enables companies to co-create products with users, ensuring greater market alignment. Brands like LEGO Ideas and Heineken’s Open Design Challenge showcase how engaging external communities leads to innovation that resonates with customers.
As industries continue to evolve, businesses that embrace open innovation gain greater agility, faster time-to-market, and a competitive edge.
The four open innovation models
Traditionally, companies relied on internal teams to generate and develop ideas. Employees, being closest to the company’s operations, were seen as the primary source of innovation. However, as industries evolve and competition intensifies, businesses are recognizing the limitations of hidden innovation and embracing open innovation models to source ideas from diverse external and internal channels (Exhibit 2).

Exhibit 3: Comparison of different ideation approaches
Modern idea management programs leverage digital tools to collect, evaluate, and implement ideas from a broader ecosystem, increasing the quality, speed, and scalability of innovation. These platforms facilitate collaboration among a global network of individuals and businesses, enabling companies to drive more impactful innovation. The four key open innovation models—internal crowdsourcing, peer sourcing, external crowdsourcing, and AI-generated ideation—enable companies to drive more impactful innovation.
1. Internal crowdsourcing and employee suggestions
Modern idea management tools facilitate collaboration among internal and external stakeholders through gamification, real-time feedback, and transparent idea-sharing platforms. This approach fosters a culture of innovation where employees feel empowered to contribute, knowing their insights can directly influence business outcomes. Companies like Google and 3M have successfully harnessed employee-driven innovation to develop groundbreaking products like Gmail and Post-it Notes.
2. Co-creation: Engaging customers, partners, and suppliers
Innovation isn’t limited to internal teams. Companies that actively engage external stakeholders—such as customers, suppliers, and business partners—gain access to real-world insights and market-driven innovations. Co-creation initiatives allow businesses to develop solutions that better align with customer needs and industry trends.
For instance, LEGO Ideas invites fans to submit and vote on new product designs, ensuring that only the most engaging and market-relevant ideas move into production. Similarly, Heineken’s Open Design Challenge sources design concepts from creative professionals, turning external insights into innovative product experiences.
3. External crowdsourcing and broadcasting challenges
By extending innovation efforts beyond immediate networks, companies can source new and innovative ideas through external crowdsourcing. For example, NASA frequently crowdsources solutions for complex aerospace challenges, gathering insights from scientists and engineers worldwide.
This approach provides access to diverse perspectives and specialized expertise, often leading to breakthrough innovations that internal teams might not have developed independently.
4. AI-generated ideation
Artificial intelligence is transforming idea generation by analyzing vast datasets, identifying trends, and suggesting innovative solutions. AI-driven systems can scan market trends, analyze customer feedback, and generate predictive insights to accelerate the innovation process.
Effective project management is crucial in AI-driven innovation, as it ensures clear project objectives and facilitates collaboration among internal and external stakeholders. By integrating AI-powered ideation into open innovation strategies, companies can enhance creativity, automate idea selection, and improve decision-making, ultimately leading to faster and more effective innovations.
How to overcome open innovation challenges
Open innovation offers businesses access to external knowledge, faster development cycles, and cost-effective R&D. However, implementing it effectively comes with challenges, including intellectual property concerns, collaboration difficulties, cultural resistance, and integration issues. Addressing these barriers is essential to maximizing the benefits of open innovation.
1. Managing intellectual property (IP) risks
One of the most significant concerns in open innovation is the protection of intellectual property. Companies fear losing control over proprietary knowledge when collaborating with external partners.
To mitigate this risk:
Establish clear legal agreements before engaging in partnerships. Contracts should define ownership, licensing terms, and revenue-sharing agreements.
Use controlled access to sensitive data, sharing only necessary information while protecting core innovations.
Companies like Tesla, which made its EV patents open-source, balance open innovation and IP control by strategically sharing technologies that benefit the broader industry while maintaining proprietary advantages in manufacturing and branding.
2. Strengthening collaboration and trust
Successful open innovation depends on strong partnerships with startups, universities, suppliers, and crowdsourcing communities. However, misaligned incentives, poor communication, and lack of trust can hinder collaboration.
To foster effective partnerships:
Define clear roles, goals, and expectations to align all stakeholders.
Use collaborative platforms that provide real-time idea-sharing, transparent discussions, and structured innovation workflows.
For example, Unilever’s Open Innovation Program works by setting well-defined challenge briefs and offering incentives to external innovators, ensuring mutual benefits for all participants.
3. Overcoming organizational resistance to change
Many organizations struggle with internal resistance to open innovation, as employees may perceive external ideas as threats or disruptions.
To build an open innovation culture:
Promote a mindset shift by demonstrating how external collaboration enhances, rather than replaces, internal expertise.
Provide training on innovation management tools to help employees integrate open innovation into their workflows.
Companies like Siemens actively encourage employees to engage in external innovation challenges, integrating open innovation into their broader R&D strategy.
4. Integrating external innovations into business operations
Even when external innovations are sourced successfully, many companies struggle to implement them effectively into existing processes.
To ensure smooth integration:
Establish dedicated teams responsible for evaluating, refining, and scaling external ideas.
Align external innovations with internal R&D roadmaps to ensure feasibility.
Use agile experimentation to test ideas quickly before full-scale implementation.
For example, LEGO Ideas integrates winning fan-submitted designs into its product portfolio through structured evaluation and market testing.
The optimal open innovation process
Open innovation enables companies to leverage external expertise, accelerate development, and drive meaningful innovation. However, without a structured process, organizations may struggle to integrate external ideas effectively. A well-designed open innovation process follows six key stages: defining objectives, sourcing ideas, evaluating contributions, co-developing solutions, implementing innovations, and measuring impact (Exhibit 3).
Exhibit 4: The optimal innovation process
Defining clear innovation challenges
The first step in open innovation is setting clear challenges that external contributors can help solve. Companies need to determine whether they aim to develop new products, improve operational efficiencies, explore emerging technologies, or address industry-wide problems. Without well-defined challenges, external contributors may struggle to propose relevant or feasible solutions.
Many companies, such as Unilever and Siemens, define their innovation challenges precisely before launching open innovation initiatives. This ensures that incoming ideas align with their business needs and increases the chances of finding viable solutions.
Open innovation platform to sourcing external ideas
Once challenges are established, companies must identify and engage the right sources of external innovation. Open innovation platforms provide structured environments where businesses can connect with external experts, startups, researchers, and the public to crowdsource solutions.
Internal crowdsourcing allows employees across departments to contribute ideas, while customer and supplier co-creation fosters practical and market-driven innovation. Public crowdsourcing platforms expand the innovation network by inviting global talent to participate, while partnerships with startups and universities provide access to cutting-edge research.
NASA, for instance, frequently uses crowdsourced innovation challenges to solve complex engineering problems, demonstrating the power of external collaboration.
Evaluating and selecting the best ideas
Not all ideas hold the same value, and companies need a structured process to assess feasibility, market potential, and alignment with corporate strategy. Cross-functional teams from R&D, marketing, and operations typically review proposals to ensure they meet both technical and commercial requirements (Exhibit 4).
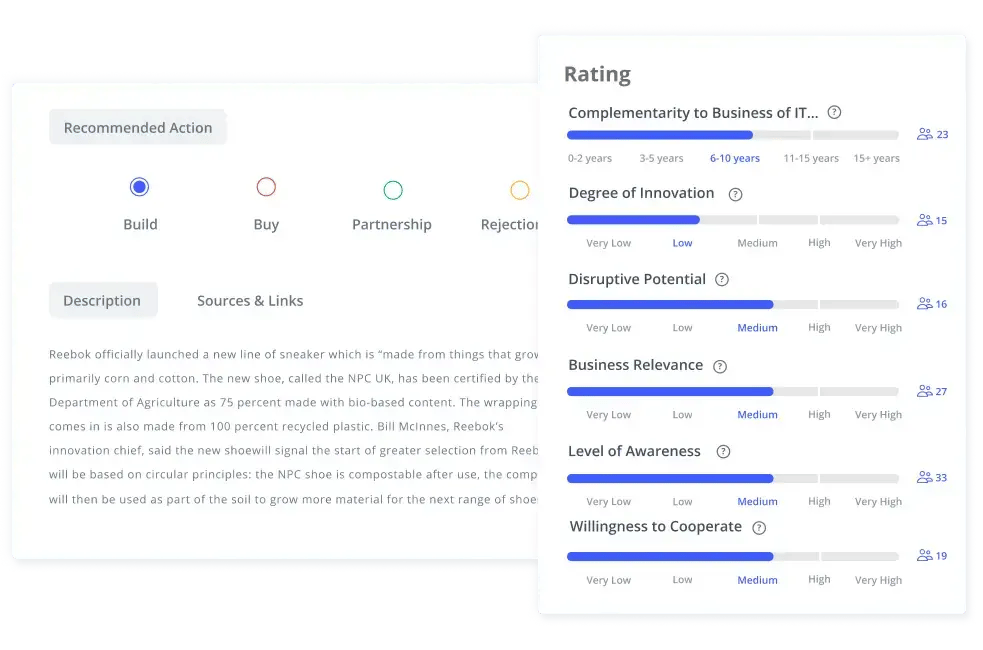
Exhibit 5: Evaluating and selecting the best ideas
AI-driven analytics can also play a role in identifying promising trends and filtering out redundant or low-impact ideas. Procter & Gamble’s open innovation program employs a rigorous evaluation framework, ensuring that only the most viable ideas move forward.
Co-develop and prototype innovations
With the best ideas selected, companies must then focus on co-developing and prototyping innovations. This phase requires strong collaboration between external contributors and internal teams. Joint development programs help refine concepts, while agile experimentation through rapid prototyping and iterative testing ensures that ideas are validated before full-scale implementation.
Intellectual property concerns must also be addressed, with clear agreements on ownership, licensing, and revenue-sharing structures. LEGO Ideas exemplifies this approach, guiding fan-designed products through a structured prototyping and market validation process before launching them commercially.
Implementing and scaling projects
Successful ideas must then be integrated into the company’s core operations. Scaling an innovation requires alignment with corporate strategy, efficient production, and supply chain integration. Internal teams must also be trained to adopt new technologies or processes.
Tesla’s open-patent strategy illustrates how a company can share its innovations with the broader industry while maintaining a competitive edge by focusing on superior manufacturing and operational execution.
Best examples of open innovation in action
Open innovation has become a crucial strategy for companies looking to stay ahead in highly competitive and rapidly evolving industries. By leveraging external partnerships, engaging with startups, and tapping into global expertise, organizations can accelerate innovation, reduce costs, and bring cutting-edge technologies to market faster.
Bosch
Bosch operates various open innovation programs that invite startups, universities, and industry professionals to contribute to its innovation pipeline. Through its Innovation Scouting and Startup Partnerships, Bosch actively collaborates with tech startups to develop next-generation solutions in AI, IoT, and smart mobility.
The Bosch Open Bosch initiative further facilitates co-creation, enabling businesses to work alongside Bosch engineers to develop market-ready products. One of the most notable examples of Bosch’s open innovation success is its involvement in AI-powered predictive maintenance. By partnering with AI startups and research institutions, Bosch developed smart sensors that enhance industrial automation.

KTM
KTM’s Pierer Innovation Platform facilitates collaboration with tech startups, research institutions, and independent engineers. Through this platform, KTM invites external innovators to co-develop cutting-edge motorcycle technologies, focusing on electric mobility, autonomous systems, and smart vehicle connectivity.
One of KTM’s most significant open innovation successes has been its development of electric motorcycles. By working with battery technology firms and alternative energy startups, KTM has advanced in sustainable transportation. The company’s partnership with external R&D teams has led to the production of high-performance electric bikes with extended battery life and enhanced energy efficiency.
Elia Group Tech Vision
Elia Group’s open innovation strategy focuses on identifying and integrating emerging energy technologies. Through its Tech Vision platform, the company seeks partnerships with startups, universities, and research institutions specializing in smart grids, AI-driven energy management, and decentralized energy solutions.

One of the most impactful results of Elia Group’s open innovation efforts is its development of AI-powered grid optimization systems. By partnering with AI and data analytics firms, Elia has enhanced its ability to predict energy demand, balance loads, and prevent grid failures.
Open innovation software and tools to accelerate performance
An open innovation platform is a digital platform that enables organizations to manage their innovation process, collaborate with external parties, and source new ideas and solutions (Exhibit 5).

Exhibit 6: Open innovation platforms to manage innovation processes
Key features of an open innovation platform include:
Seamless collaboration with internal and external innovators
Effective open innovation software relies on seamless communication between employees, customers, startups, and research institutions. Modern platforms provide virtual workspaces, discussion forums, and real-time feedback tools, allowing teams to refine ideas collaboratively.
Collaboration features ensure that internal stakeholders can evaluate, develop, and build upon external contributions, eliminating silos between departments and fostering cross-functional innovation.
Secure data management and intellectual property protection
One of the primary concerns in open innovation is intellectual property (IP) security. Organizations must ensure that external ideas are safeguarded, tracked, and fairly credited while maintaining proprietary control over their innovations.
Leading open innovation platforms offer secure access controls, permission-based sharing, and IP agreements to define ownership rights and licensing structures.
External portals for easy idea submission
To maximize participation, open innovation platforms provide external portals where contributors can submit ideas, respond to challenges, and track their proposals. These portals simplify the process by offering customizable submission forms, templates, and guided prompts, ensuring that submissions meet evaluation criteria.
Companies using these platforms can also integrate gamification elements, leaderboards, and incentive programs to boost engagement.
Automated workflows and notification systems
Managing a high volume of ideas efficiently requires structured workflows, project management, and automated notifications. Open innovation platforms streamline the innovation process with customizable approval pipelines, automated idea scoring, and decision-tracking tools (Exhibit 6).

Exhibit 6: Customizable approval pipelines to streamline the innovation process
Integrated notification systems keep stakeholders informed about submission status, evaluation progress, and implementation decisions.
How to get started with open innovation today
The ITONICS Innovation OS is a comprehensive platform designed to capture, share, and bring valuable ideas to production.
Streamline idea management: Managing a high volume of ideas from various sources can be overwhelming. ITONICS allows you to capture, evaluate, and prioritize ideas from across the organization, including customers and partners, all in one structured process.
Accelerate time-to-market: Gain unprecedented efficiency in innovation. The ITONICS Innovation OS saves time, reduces efforts, and accelerates time-to-market. When speed matters and time is money, reducing any administrative burden is what lets innovation leaders excel.
Monitor progress in real time: Stay on top of execution with dashboards and progress tracking. ITONICS lets you see how the innovation strategy unfolds across all departments, projects, and teams. Quickly identify roadblocks, monitor performance against key milestones, and keep execution aligned with strategic priorities.
FAQs on open innovation
What is open innovation?
Open innovation is a business strategy that leverages external knowledge, ideas, and technologies to foster innovation. Unlike traditional closed R&D, where companies rely solely on internal expertise, open innovation encourages collaboration with startups, universities, suppliers, customers, and even competitors to accelerate product development, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
What are the different types of open innovation?
The main types of open innovation include:
- Inbound open innovation: Bringing in external ideas, technologies, or startups
- Outbound open innovation: Sharing or licensing internal innovations to others
- Coupled open innovation: A mix of both inbound and outbound collaboration
Why is open innovation important?
Open innovation allows companies to expand their innovation capacity, access fresh perspectives, reduce R&D costs, and bring new products and services to market faster. It helps businesses stay competitive in rapidly evolving markets by tapping into external knowledge and ecosystems.
What are some examples of open innovation in practice?
Examples include running innovation challenges with customers, collaborating with startups, setting up accelerator programs, launching co-creation platforms, or partnering with universities. Companies like LEGO, Bosch, BMW, and Unilever have successfully applied open innovation strategies.
How do you implement open innovation in a company?
Start by defining clear innovation goals and identifying the external partners or communities you want to involve. Establish open channels for collaboration (e.g. idea submission platforms like ITONICS for open innovation, co-creation workshops), ensure IP protection and data sharing frameworks, and use software to manage ideas, contributions, and evaluation.
What tools or software can support open innovation?
Open innovation software helps companies run idea challenges, manage submissions, collaborate with external stakeholders, and evaluate concepts at scale. Platforms like ITONICS provide features for scouting, ideation, evaluation, and trend integration—all in one secure environment.
How can enterprises manage open innovation with partners and customers?
Enterprises manage open innovation by using digital platforms that support secure idea submission, structured evaluation workflows, and real-time collaboration with external contributors. With clearly defined challenges, transparent governance, and role-based access, organizations can engage partners and customers at scale, while protecting IP, tracking progress, and accelerating co-development.
How do digital tools enable bottom-up innovation in enterprise?
Digital platforms enable bottom-up innovation by empowering employees to submit ideas, collaborate across functions, and engage in transparent evaluation processes. Allowing to turn internal crowdsourcing into a structured, organization-wide innovation capability.




