Improperly capturing new solutions or simply letting opportunity-rich concepts slip through the cracks too early in the innovation journey can be the difference between an organization that fails to innovate and grow, and an industry leader that is not only adapting to change but shaping it. This is the difference between organizations that rely on manual and fragmented processes to collect and track ideas, and those that employ a structured and centralized idea management system.
In this article, we will explain how to implement effective idea management processes in your organization based on three fundamental pillars, along with the benefits of a dedicated idea management system.
What is idea management?
Idea management is sometimes used interchangeably with the term innovation management. However, there are distinct differences, and understanding how each fits into the big picture can promote more seamless execution throughout end-to-end innovation and produce better outcomes.
Idea management refers to the structured process of generating, evaluating, and improving ideas that contribute to an organization’s innovation strategy and growth. This includes prioritizing and implementing ideas. Idea management can occur through a centralized or decentralized process. Centralized idea management allows an entire organization to engage in the process, whereas decentralized idea management allows different teams or business units to manage their own ideas.
In contrast, innovation management consists of much more than just innovative ideas. Innovative management operationalizes and connects strategic foresight, idea management, and portfolio management in an end-to-end process that guides and governs innovation activities from strategy to execution while fostering an innovation culture.
Why is idea management important?
To understand the importance of idea management, it is helpful to contextualize it within the big picture, as mentioned above. Our ITONICS Big Picture illustrates the end-to-end innovation management process and the key activities that serve to answer three strategic questions: Where to Play (strategic foresight), How to Win (idea management), and What to Execute (portfolio management).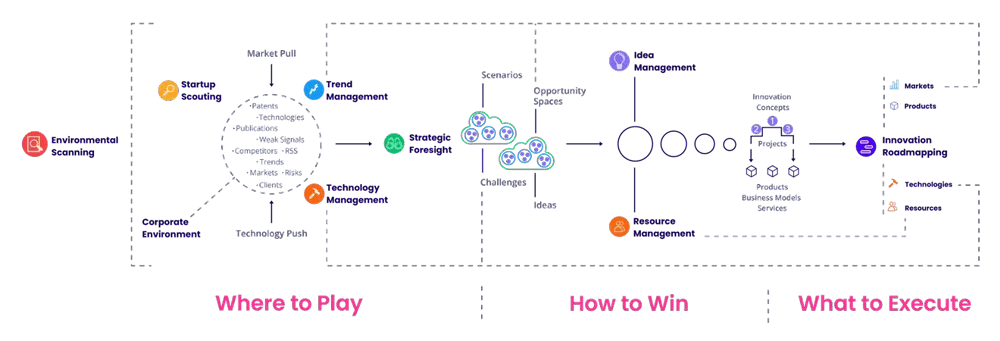
Effective idea management within an organization reveals How to Win. It does so by connecting the strategic imperatives identified in the Where to Play phase of innovation management to the What to Execute phase, which focuses on prioritization and implementation.
Idea management bridges this gap in two ways:
- By providing a structured process for generating, refining, and validating ideas, idea management ensures that the strategic opportunities you have identified are appropriately exploited.
- By prioritizing valuable ideas and providing workflows to move them into innovation portfolios, idea management ensures that your best ideas are adequately supported, resourced, and implemented.
As a result, idea management not only fuels growth but looks to maximize new value created through innovation management. In this way, an effective idea management system offers organizations the possibility to:
- Strategically link ideation efforts to viable future business opportunities.
- Support a unified vision of organizational strategy.
- Harness the power of collective intelligence.
- Better inform resource allocation and investment decisions.
- Respond to market needs timeously.
→ Product Fact Sheet: ITONICS Campaigns for Successful Idea Management
3 fundamental pillars of effective idea management
There are three fundamental pillars that support effective idea management:
- Definition
- Ideation
- Value Realization
.webp?width=1000&height=157&name=effective-idea-management-1%20(1).webp)
1. Definition
The objective of the first idea management pillar is to define the process requirements, action plan, and key performance indicators (KPIs) of your ideation campaign and overall idea management process.
Having a clearly defined approach from the very beginning of ideation ensures that idea challenges and campaigns run efficiently. A framework for idea submission ensures everyone is on the same page, boosts employee engagement, and improves the quality of ideas submitted. In turn, this increases the probability of identifying truly great ideas that meet innovation objectives.
This pillar focuses on defining an idea workflow or phase-gate process, roles and responsibilities, engagement tactics, and the communication management approach. Because it is imperative to establish a strong idea management foundation before initiating ideation, we will go into each of these activities in more detail.
Idea workflows
An idea workflow is a phase-gate process that divides the ideation process into distinct phases, with each phase representing a specific milestone or checkpoint. At the end of each phase, a gate review or decision point occurs where stakeholders assess the progress, risks, and potential value of the idea. The gate review determines whether the idea should proceed to the next phase or be modified or terminated.
.webp?width=769&height=320&name=effective-idea-management-2%20(1).webp)
|
Phases of an idea workflow often involve specific tasks and requirements that must be fulfilled before an idea proceeds to the next phase. Transparently outlining these tasks and requirements reduces subjective biases and ensures only the most valuable ideas move forward. |
Gates are checkpoints for evaluating ideas against predetermined criteria to inform whether an idea should proceed to the next phase, be modified, or be terminated. These criteria differ depending on the phase but could include relevance, novelty, imitability, complexity, cost-benefit ratio, and many more factors. |
Your idea workflow and the number and scope of its various phases and gates should be aligned with the specific needs and objectives of your idea management program. However, it is good advice to keep your idea workflows straightforward and easy to follow. Avoid unnecessary complexity or detail, and focus on the key activities and decision points that are critical to your idea management program.
Example of an idea workflow with phases, gates, and evaluation criteria:
.webp?width=827&height=663&name=effective-idea-management-3%20(1).webp)
→ Cheat Sheet: How to Rate Ideas
Roles and responsibilities
Defining clear roles and responsibilities ensures that each team member knows and is accountable for their specific tasks and contributions to the idea management program. This clarity streamlines the workflow, prevents duplication of efforts, and minimizes confusion, leading to greater overall efficiency.
By providing a clear structure and purpose to each team member's contributions, organizations can ensure that the right people are involved at the appropriate stages of their idea management program.
Common roles and responsibilities in the idea management process:
.webp?width=765&height=517&name=effective-idea-management-4%20(1).webp)
Engagement tactics
Engagement tactics in idea management are strategies and approaches used to actively involve stakeholders in the ideation process. These tactics drive successful idea management initiatives and foster an organization’s innovation culture.
Typically, the best ideas are generated and brought to life when multiple and diverse perspectives, competencies, and expertise are involved. But boosting engagement in today's organizations looks different than the traditional suggestion box and brainstorming session that tend only to capture ideas from a few people. To truly unleash the creative potential of your employees, partners, experts, and possibly even customers, it is necessary to sustain meaningful engagement throughout the process.
Captivate participants' attention and inspire them to collaborate without reserve using best-practice engagement tactics, including:
- Align with purpose. Connect efforts to a greater organizational purpose.
- Emphasize organizational values. Uphold core values throughout the idea management process.
- Encourage growth. Provide opportunities for personal and career growth.
- Acknowledge and appreciate. Recognize contributions and reward winning ideas.
- Communicate openly and frequently. Promote transparency throughout the idea management process.
- Build on ideas. Allow for candid and constructive feedback.
- Empower ownership. Instill a sense of accountability.
- Foster creativity. Provide digital and/or physical spaces that inspire creative participation.
Communication management
Communication within the idea management process refers to the strategic planning, execution, and monitoring of communication activities related to an idea campaign, its objectives, and outcomes. It involves establishing clear and effective communication channels and collateral to facilitate the flow of information, ideas, and feedback among all stakeholders involved in the ideation process.
A clear communication plan is critical to gain support from and align all stakeholders within the process. It is essential to build a communications plan, irrespective of the scale of the project, to ensure everyone is aligned on the purpose, various activities, and expectations within the process.
A comprehensive communication plan should outline what, when, and how the information will be shared with specific audiences at key intervals. A communication plan should detail the following information:
- Stakeholder or audience: Who are we addressing?
- Message or topic: What is the key message we want to convey?
- Communicator: Who would be best to relay this information?
- Schedule or frequency: When or how often should we communicate with the various audiences?
- Delivery method: What channels would be most effective to deliver the information?
- Feedback: How can we gather additional inputs and feedback to ensure a dialogue?
2. Ideation
The objective of this pillar is to encourage your innovation community, including employees and/or external contributors, to actually generate and submit ideas and outline the what, why, and how.
Ideation is the actual idea generation phase in which new ideas are submitted as part of a campaign. Generating ideas in collaboration with a diverse group of stakeholders helps to unleash creative potential. And nurturing this creative potential through systematic idea management leads to not only more ideas but more high-quality and innovative ideas for new features, products, services, and business models that will ultimately drive innovation.
Often, ideas are explored as potential solutions to specific challenges or customer pain points, and the ideas generated are based on trends, emerging technologies, expectations associated with existing products, or unmet needs that may call for radically new ideas.
There are several different approaches to ideation, including closed or open innovation, ideation challenges, and workshops. Within these approaches, organizations can employ various idea generation methods depending on their specific requirements and innovation objectives.
- Crowdsourcing: Crowdsourcing is an idea generation method that involves leveraging the power of a specific crowd or a defined group of individuals to contribute ideas, insights, or solutions to a problem or challenge.
- TRIZ: TRIZ stands for “theory of inventive problem-solving.” It provides a systematic approach to problem-solving by providing data on similar past projects and recognizing patterns in inventive solutions.
- Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a popular technique used by organizations for generating creative ideas. The purpose of brainstorming is to encourage free thinking, open discussion, and the exploration of unconventional ideas.
- Pyramid search: The pyramid search technique is an idea generation method that sources ideas in analogous domains or industries. It involves an iterative process of expert identification and referral until the top of a “knowledge pyramid” is reached, and then the process begins again in an analogous domain.
→ Product Fact Sheet: ITONICS Open Innovation for Activating Collective Intelligence
3. Value realization
The objective of this pillar is to enrich and grow ideas, prioritizing the most impactful ideas that support your strategic objectives and transferring them to your innovation portfolio. It also involves assigning ownership to business functions with the necessary resources needed to bring those ideas to fruition.
Value realization involves the refinement and validation of ideas. This relies on monitoring and measuring KPIs to inform iterative improvement. To apply KPIs, you need a clear process in place that will allow you to collect actionable data, gather feedback, and derive valuable insights related to your ideas.
There are several tools for idea refinement that have various functions and strengths:
- Design thinking. Design thinking is a problem-solving approach and a mindset that focuses on understanding and addressing the needs and desires of users or customers. It emphasizes empathy, collaboration, experimentation, and iteration to create and implement innovative solutions.
- Personas: Personas involve creating fictional characters or user profiles representing specific segments of a company's target audience or customer base. These personas are designed to capture the characteristics, needs, goals, behaviors, and preferences of real users or customers.
- Kano model: The Kano model, or Kano analysis, is a technique used in the field of quality management and customer satisfaction to prioritize and classify customer needs and requirements. It provides a structured approach to making strategic decisions about product or service development.
- Morphological analysis: Morphological analysis is a creative problem-solving technique that involves breaking down a complex problem into its constituent parts or attributes and exploring various combinations of these attributes to generate and refine new ideas and solutions.
- Value proposition canvas: A value proposition canvas is a strategic tool that helps organizations refine their ideas for corporate innovation by understanding and designing compelling value propositions for their target customers. It is a visual framework that enables companies to analyze the fit between their products or services and the needs and desires of their customers.
How ITONICS can help you with effective idea management
There are several idea management tools available that focus on the three foundational pillars discussed above: definition, ideation, and value realization. While it's easy to find idea management software that creates a phase-gate process or a submission portal for idea collection, true innovation leaders need an idea management platform that provides the essential capabilities and framework to integrate and strengthen all three pillars—to move ideas forward systematically and decisively.
The ITONICS Innovation OS provides an end-to-end idea management software solution that allows you to manage ideas from inception to execution. With ITONICS Campaigns, you can define custom idea workflows and evaluation criteria. Use ITONICS Open Innovation to involve clients, external experts, startups, and potential partners in generating solutions for short-, mid-, and long-term challenges.
KPI and activity dashboards, interactive visualizations, and analytical tools allow you to monitor and rank ideas. Encourage participation with gamification, nudging, and customized submission platforms. Establish roles and permissions, operate within a clearly-defined governance framework, and build the transparency and structure needed to drive innovation in your organization.
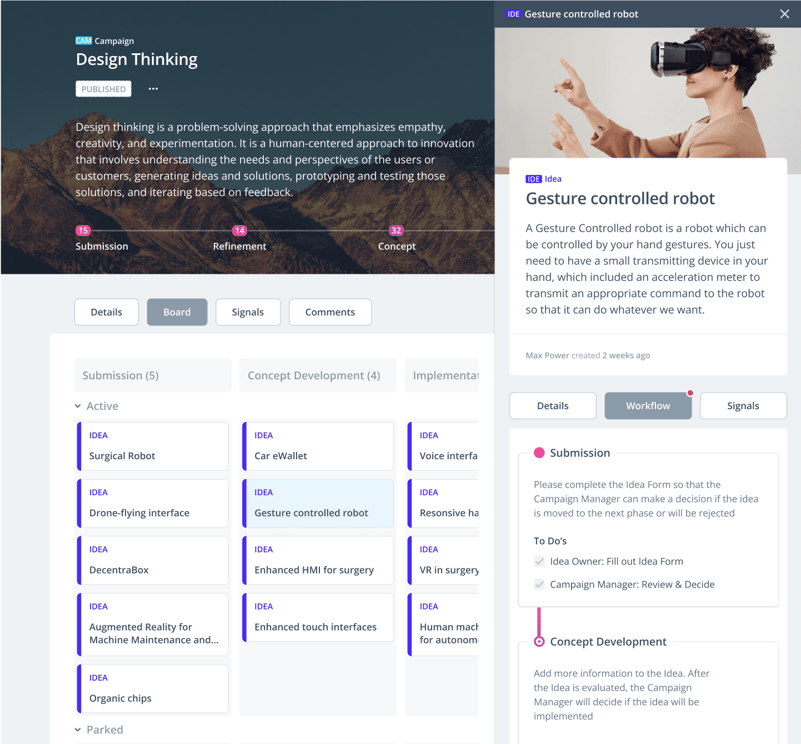
The ITONICS Innovation OS is much more than just idea management software. It anchors ideation in a single point of truth to bring ideas to life faster. And unlike fragmented innovation software solutions, it links your ideation activities to foresight intelligence and portfolio to maximize your innovation potential and deliver on your strategic goals with speed and agility.
To learn more about how ITONICS can help you unlock the power of ideas and collaboration, sign up for a free demo and see the Innovation OS in action.





